Patient Safety Collaborative (Greater Manchester PSC)

Worldwide, patient safety incidents cause death and disability. Patient safety is about maximising the things that go right and minimising the things that go wrong for people receiving healthcare. It is integral to the NHS’s definition of quality in healthcare, alongside effectiveness and patient experience.
England’s 15 Patient Safety Collaboratives (PSCs) play an essential role in identifying and spreading safer care initiatives from within the NHS and industry, ensuring these are shared and implemented throughout the health and care system.

The Greater Manchester (GM) PSC is commissioned to deliver NHS Englnd’s (NHSE) National Patient Safety Improvement Programmes (NatPatSIPs) for the people of Greater Manchester. As a key component of the NHS Patient Safety Strategy, the NatPatSIPs address the most important safety issues and embed improvement methods and measurement into management systems. Collectively they form the largest safety initiative in the history of the NHS.
We work with our local Integrated Care System (ICS) to develop and spread innovative improvement methods, which are systematic, evidence-based and measurable. QI approaches include the Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) Model for Improvement.
Current programmes
(click the image to read more)

Managing Deterioration Safety Improvement Programme
View Project
Maternity and Neonatal Safety Improvement Programme
View Project
System Safety Improvement Programme
View Project
Medicines Safety Improvement Programme
View Project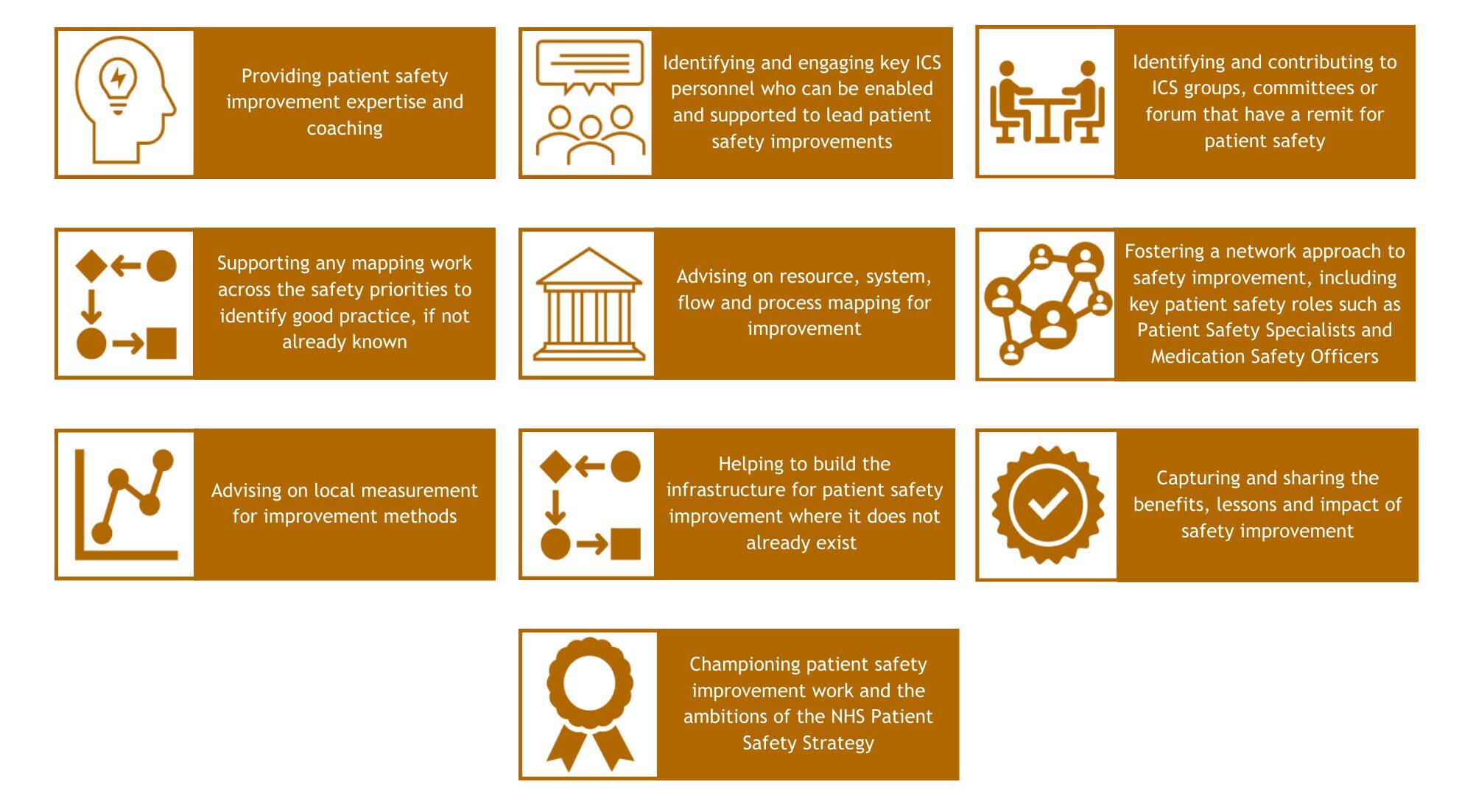
National Patient Safety Improvement Programme (NatPatSIP)

The National Patient Safety Improvement Programmes aim to support and encourage a culture of safety, continuous learning and improvement across the health and care system, helping to reduce the risk of harm and make care safer for all.
The programmes support systems to test and spread effective safety interventions and strategies, learn from excellence and continuously improve, by implementing the following:
- Culture: promote positive safety culture, encouraging staff to gain insight and share learning from good and poor practice
- Evidence-based improvement: support evidence-based, quality improvement (QI) methodology, ensuring change is consistently measured and evaluated
- Quality improvement (QI) capability: grow QI capability in trusts and local healthcare systems so they can continue to improve
- System-level change: enable regional and local health systems to identify improvement priorities and share learning.
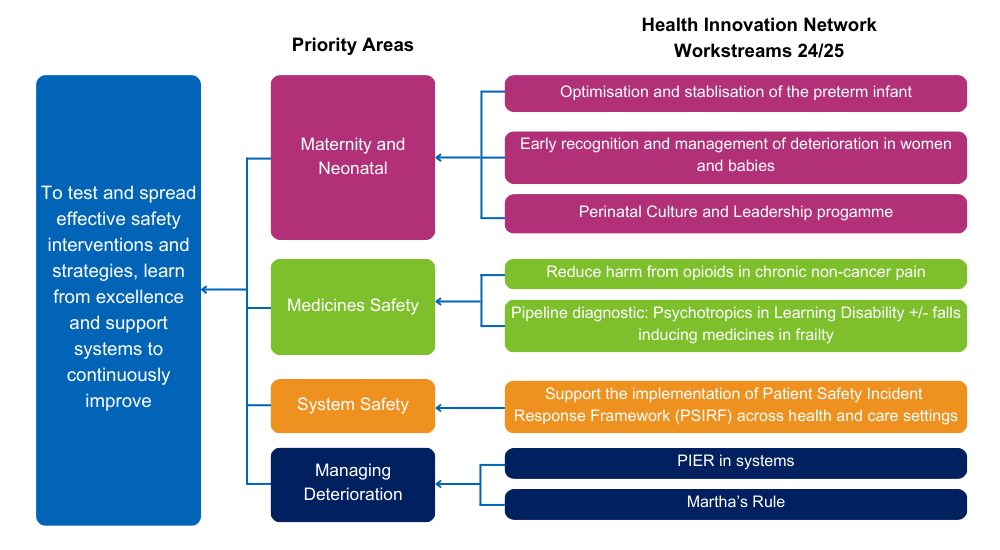
For 2024-25 our work is focused across four priority safety areas, as shown in the driver diagram below:
Archived programmes
(click the image to read more)
Case Studies
To find out more about the PSC contact:[email protected]
You can find out more about the National Patient Safety Improvement Programmes and view more resources





